Hydrogen is considered as a globally accepted renewable energy carrier to satisfy the growing demand for clean energy. Photocatalytic hydrogen production from water splitting on photocatalysts under solar radiation represents a promising route to produce hydrogen, which has attracted increasing attention since the groundbreaking work of Fujishima and Honda on photoelectrocatalytic H2 evolution over a TiO2 electrode. Charge separation and surface reaction are the two crucial steps in heterogeneous photocatalysis process for the semiconductor photocatalyst system to achieve high quantum efficiencies. Loading oxidation and/or reduction cocatalysts on the surface of a semiconductor is a widely applied and effective strategy for efficient charge separation and creation of surface redox reaction sites. We designed and prepared on a facile template-assisted ALD approach to synthesize a new porous tubular CoOx/TiO2/Pt photocatalysts with spatially separated dual cocatalysts (Pt and CoOx) for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production from aqueous methanol solution. In this work, porous TiO2 nanotubes were obtained using carbon nanocoils (CNCs) as sacrificial templates, in which Pt and CoOx nanoclusters are separately decorated on the inner and outer surface of porous TiO2 nanotubes, respectively. Pt nanoclusters acting as electron collectors and active sites for reduction reaction are deposited on the inner surface of porous TiO2 nanotubes, while CoOx nanoclusters acting as hole collectors and active sites for oxidation reaction are deposited on the outer surface of porous TiO2 nanotubes. Upon generation from porous TiO2 nanotubes, electrons and holes flow inward and outward TiO2 nanotubes, respectively, accumulate on the corresponding cocatalysts, and then take part in the redox reactions.
In recent years, ALD has been widely applied in catalysis area, which has obvious advantages in synthesis of catalysts with ultra-fine nanoparticles, confined catalysts and tandem catalysts. One of the advantages of ALD in catalyst preparation is that the particle size and loadings of metals can be precisely controlled by simple tuning cycle numbers. With ultra-low contents of noble Pt (0.046 wt.%) and CoOx (0.019 wt.%) deposited both with one ALD cycle, the CoOx/TiO2/Pt photocatalysts can achieve remarkably high photocatalytic efficiency (275.9 μmol h-1), which is nearly five times as high as that of pristine TiO2 nanotubes (56.5 μmol h-1). The highly dispersed Pt and CoOx nanoclusters, porous structure of TiO2 nanotubes with large specific surface area, and the synergetic effect of the spatially separated Pt and CoOx dual cocatalysts contribute to the excellent photocatalytic activity. In addition, the hydrogen production rates for the reference photocatalysts TiO2/Pt-CoOx and Pt-CoOx/TiO2 were determined to be about 131.7 μmol h-1 and 73.7 μmol h-1, respectively, which were much lower than that of CoOx/TiO2/Pt. The corresponding results have been published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 816-820.
The general and facile method based on template-assisted ALD can be potentially applied to synthesize other kinds of photocatalysts (e.g., CoOx can be changed as NiO or MnOx), which provides important guidance for the design and preparation of efficient photocatalysts. We appreciate the financial support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (21203229, 21403272, and 21673269), the Hundred Talent Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Hundred Talent Program of ShanXi Province, the ShanXi Science and Technology Department, Department of Human Resource and Social Security of ShanXi Province, and Natural Science Foundation of ShanXi Province (2014011012-1 and 2015021046).
氢能作为一种环境友好的清洁能源被认为是可替代化石燃料的重要能源。光催化分解水制氢是一种非常有前景的绿色制氢途径。影响光催化制氢效率的一个主要因素是电子和空穴的分离效率低。在半导体材料表面负载产氢或/和产氧助剂(例如,Pt,Pd,CoOx,NiO)可有效提高电子和空穴的分离效率,尤其是含双助剂的光催化剂比含单助剂的光催化剂显示更佳的催化性能。但对于大多数双助剂的光催化剂而言,助剂是随机分布在半导体材料表面的,这就使得电子和空穴的溢流方向是随机的,从而增加了电子空穴的复合几率。
近年来,原子层沉积(Atomic Layer Deposition,ALD)技术越来越受催化领域研究者的关注。其在制备超细纳米催化剂、催化剂表界面调控、限域的催化剂及多功能串联催化剂等方面体现出突出的优势(Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 9006-9100;Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 7081-7085)。最近,本课题组与郑占峰研究员合作,利用ALD设计并制备了具有空间分离结构的Pt和CoOx双助剂的多孔TiO2纳米管光催化剂。以碳纳米螺旋(CNC)为模板,在CNC表面先后沉积Pt纳米簇/单原子和TiO2层。经过空气中焙烧去除CNC模板,同时非晶态的TiO2结晶收缩转变为多孔的锐钛矿TiO2,得到多孔TiO2/Pt光催化剂。然后再利用ALD沉积CoOx纳米簇在TiO2纳米管的外壁,最终得到多孔TiO2负载空间分离的Pt和CoOx双助剂的CoOx/TiO2/Pt光催化剂。
在紫外光照条件下,电子和空穴分别溢流到管内壁的Pt和管外壁的CoOx(分别发生相应的产氢半反应及甲醇氧化反应),从而提高了电子和空穴的分离效率及相应的光催化产氢活性。研究结果表明,当Pt和CoOx的ALD沉积循环数分别为1时,相应的负载量分别为0.046%和0.019%时,所制备CoOx/TiO2/Pt具有最佳的光催化产氢活性(275.9 μmol h-1),是TiO2/Pt活性的1.5倍(185.9 μmol h-1)及空白多孔TiO2纳米管的5倍(56.5 μmol h-1)。此外,所制备的空间分离的双助剂光催化剂CoOx/TiO2/Pt比两种金属随机分布在管内(TiO2/Pt-CoOx: 131.7 μmol h-1)及管外(Pt-CoOx/TiO2: 73.7 μmol h-1)的催化剂也显示出更高的催化活性。相关结果近期发表在Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. , 2017, 56, 816-820。
该方法具有普适性,可以用来合成其他体系的光催化剂(例如,将CoOx替换为NiO、RuO2及MnOx等),为未来高效光催化剂的设计及制备提供了重要的科学参考。
该项目得到国家自然科学基金、中国科学院百人计划、山西省百人计划的资助与支持。
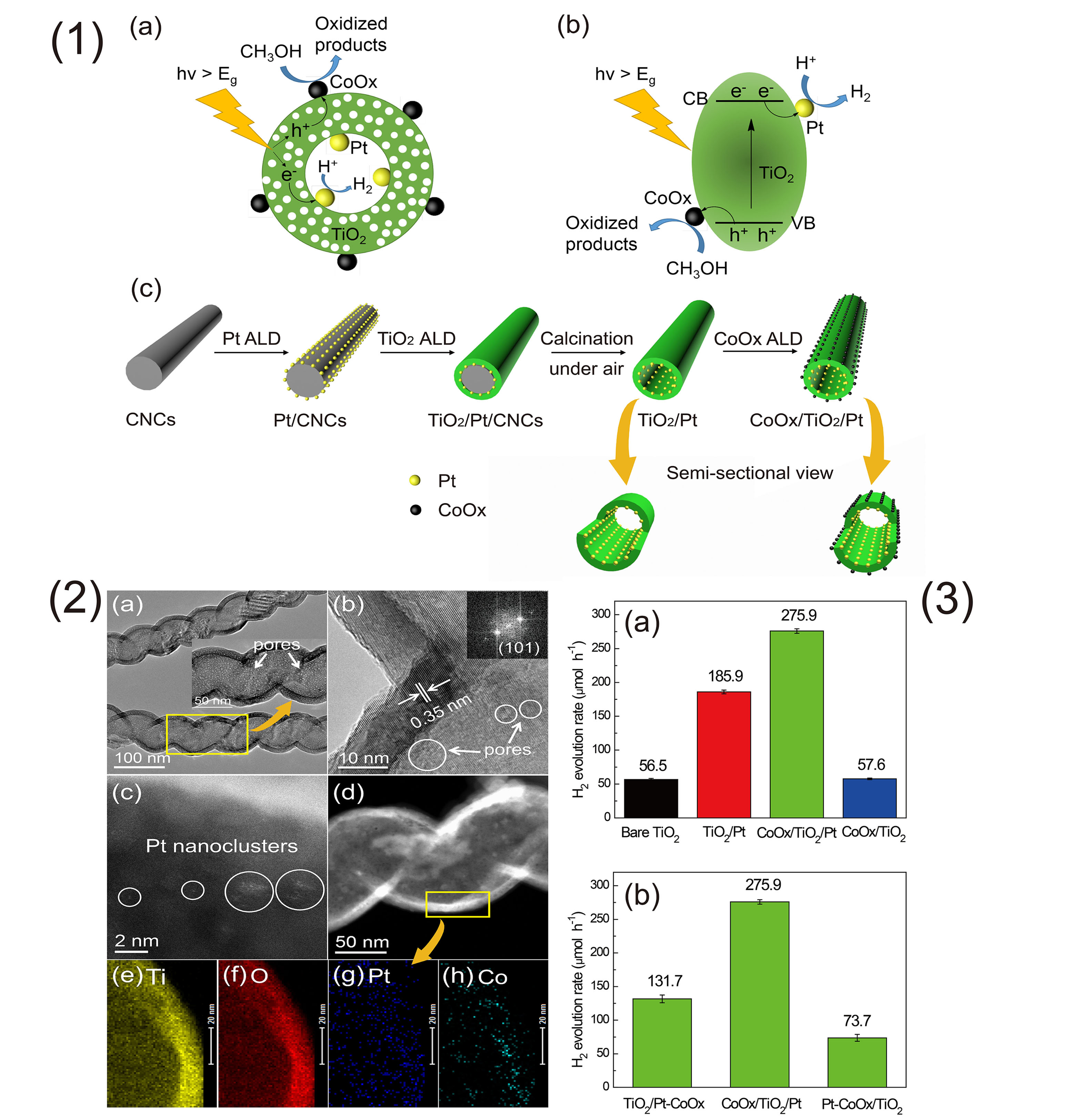
图1. CoOx/TiO2/Pt的光催化产氢机理:(a)反应过程;(b)光催化剂的能带结构;(c) TiO2/Pt及CoOx/TiO2/Pt光催化剂的合成示意图及半截面对比示意图。图2. CoOx/TiO2/Pt的(a) TEM及(b) HRTEM图;(c) CoOx/TiO2/Pt的原子分辨率HAADF-STEM图;(d-h) CoOx/TiO2/Pt的STEM图及EDS面扫描分析图。 图3. 不同催化剂的光催化性能对比。反应条件:200 mL的15 vol.% CH3OH-H2O溶液;催化剂用量0.035 g;紫外光照强度:35 mW cm-2。Pt和CoOx的沉积循环数分别为1
原文链接:http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201611137/full
?
903 Group, Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, All Rights Reserved
联系电话:0351-4040081 邮箱:qinyong@sxicc.ac.cn 地址:山西省太原市桃园南路27号
Address: 27 South Taoyuan Road, Taiyuan, Shanxi, P.R.China Tel: 0351-4040081 Email: qinyong@sxicc.ac.cn

 当前位置:
当前位置: